FSMO Roles play a crucial role in managing the overall structure of the network in Microsoft Active Directory. If you are a professional windows server administrator, you must understand FSMO roles and its functionality. What exactly are FSMO roles and why are they so important in an Active Directory?
We will walk you through everything you need to know about FSMO roles, their types, how they work and how to manage them effectively.
In This Page
You must understand Active Directory before we dive into FSMO roles.
Active Directory is like a directory service which is developed by Microsoft, It stores information about users, computers and other network devices within a virtual security boundary. Active Directory acts like a phone book for your network which makes easier to manage users, permissions and other resources.
If there is no Active Directory, it would have been a nightmare to manage large networks and all resources. FSMO roles ensure that certain critical functions within Active Directory are always available and operational.
What Are FSMO Roles?
FSMO stands for Flexible Single Master Operations. These are special roles assigned to specific servers in an Active Directory environment to handle certain critical tasks.
Unlike normal domain controllers, FSMO role holders perform unique operations that must be handled by only one domain controller at a time.
Why Are FSMO Roles Required?
There would be conflicts and inconsistencies when making changes to the Active Directory database without FSMO roles. FSMO roles ensure that no two domain controllers perform the same task at the same time.
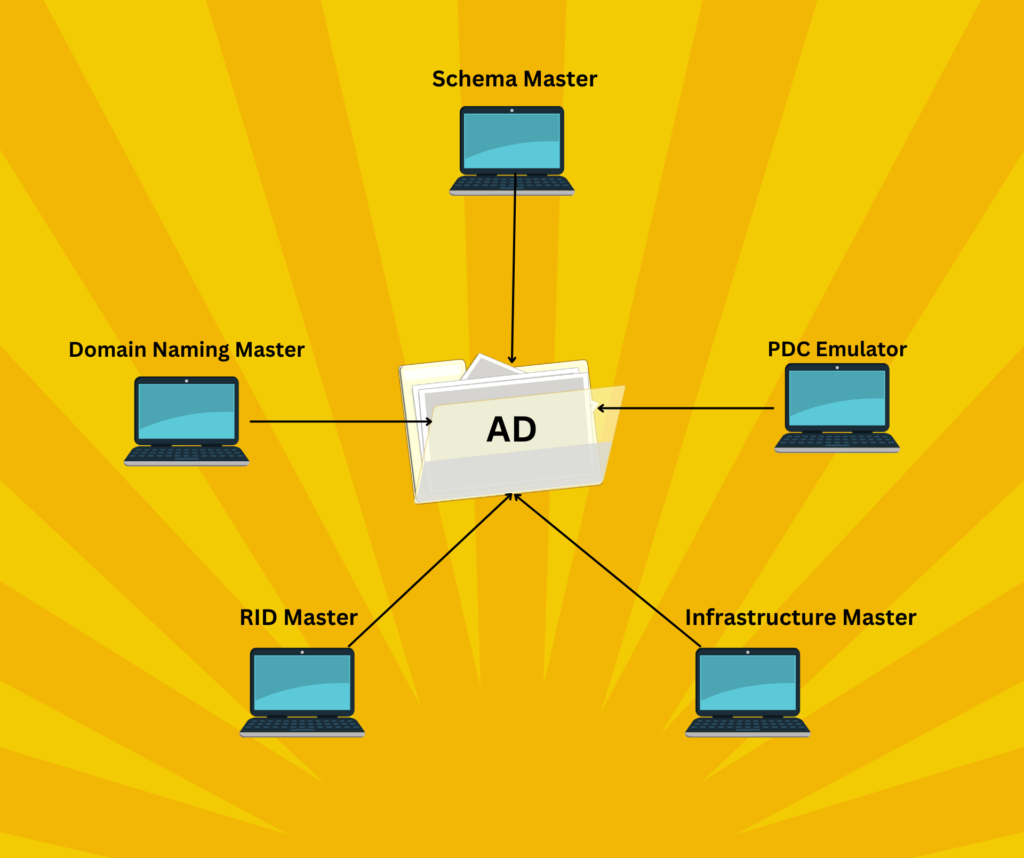
Types of FSMO Roles in Active Directory
There are five FSMO roles, categorized into two types:
1. Forest-Wide FSMO Roles
- Schema Master
- Domain Naming Master
2. Domain-Wide FSMO Roles
- RID Master
- PDC Emulator
- Infrastructure Master
Detailed Explanation of FSMO Roles
Let’s break down each FSMO role in detail.
1. Schema Master
The Schema Master controls updates and modifications to the Active Directory schema. If you want to add new attributes or object types to Active Directory, the schema master is the only server that can handle this task.
- Purpose: Manages the Active Directory schema
- Location: Only one Schema Master per forest
- When to Transfer: When the current Schema Master server is down or needs replacement
2. Domain Naming Master
The Domain Naming Master is responsible for managing domain names in the entire Active Directory forest.
- Purpose: Prevents duplicate domain names
- Location: Only one Domain Naming Master per forest
- Common Tasks: Adding or removing domains
3. RID Master
The RID Master (Relative Identifier Master) allocates RID pools to domain controllers to create unique security identifiers (SIDs) for users, groups, and computers.
- Purpose: Manages unique ID creation
- Location: One RID Master per domain
- Common Issues: RID Pool depletion
4. PDC Emulator
The PDC Emulator (Primary Domain Controller Emulator) is one of the most critical FSMO roles. It handles:
- Time synchronization
- Password changes
- Group policy updates
Without the PDC Emulator, users might face login issues or outdated passwords.
5. Infrastructure Master
The Infrastructure Master updates references from objects in other domains. It ensures that object names are consistent across different domains.
- Purpose: Manages cross-domain object references
- Location: One Infrastructure Master per domain
- Limitation: Should not be on a Global Catalog server
How to Transfer FSMO Roles
FSMO roles can be transferred from one domain controller to another using two methods:
- GUI Method
- Command Line Method
GUI Method
- Open Active Directory Users and Computers
- Right-click the domain name
- Go to Operations Masters
- Select the role to transfer
Also Learn Microsoft Deployment Toolkit
How to Seize FSMO Roles
Seizing FSMO roles is done when the current FSMO role holder is permanently offline. This method should only be used as a last resort.
Steps to Seize FSMO Roles
- Open Command Prompt
- Type: ntdsutil
- Connect to the server
- Use the seize command
Example :
seize pdcBest Practices for FSMO Roles Management
- Always back up Active Directory
- Monitor FSMO role holders regularly
- Use proper disaster recovery plans
Conclusion
FSMO roles are the backbone of Active Directory, it ensures the critical tasks are performed without conflict. Understanding and managing these roles effectively can prevent many network issues and improve the stability of your domain environment. By following best practices, you can ensure that your FSMO roles are always in top shape.
FAQs
1. What happens if FSMO roles fail?
If FSMO roles fail, certain Active Directory operations like password updates or domain name management will stop working.
2. How many FSMO roles can one server hold?
A single server can hold all five FSMO roles, but it’s best to distribute them across multiple servers.
3. How do I check FSMO roles?
You can use the netdom query fsmo command to check which server holds FSMO roles.
4. Can I transfer FSMO roles without downtime?
Yes, FSMO roles can be transferred without any downtime.
5. Is it necessary to back up FSMO role holders?
Yes, regular backups are crucial to prevent data loss.




